|
|
Basic concept of gas turbine |
|
Gas turbine is a kind of internal combustion
engine that extracts power directly from the combusted hot gas. The main
difference from a steam turbine is that the power is directly derived
from the combusted gas, not from the steam boiled by the combusted gas. How it worksA gas turbine requires the very precise manufacturing process, but its basic component is simple.
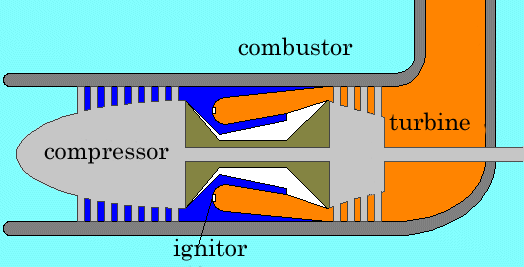
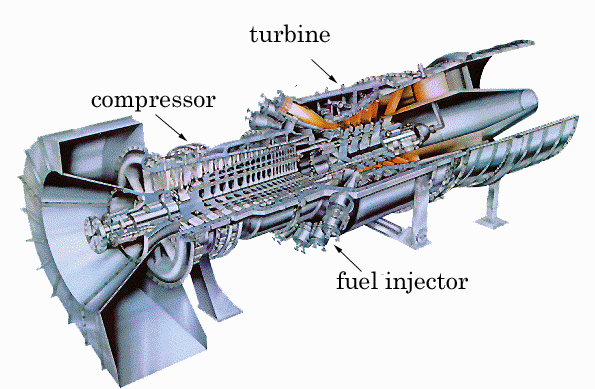
The schema above shows three major componets, the
compressor, the combustor and the turbine. The compressor is
usually consists of the core shaped cylinder with many fan blades attached
in rows The high speed rotation of these fan blades compresses the air and
send it to the combustor. In the combustor, fuel is injected in to the compressed
air and ignited. Then combusted high pressure hot gases enter into
the turbine section, spin the turbine and the exhausted gases are
released into the atmosphere. The compressor and the turbine are directly coupled
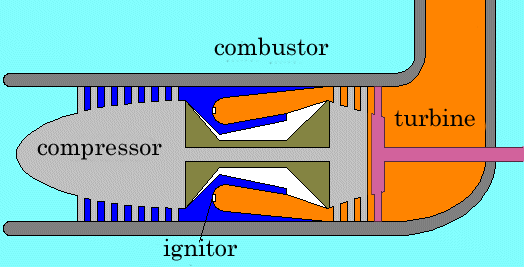
and turn as the single unit. In the next schema, a turbine is separated into two part, each can spin independently. The compressor and the left turbine turn as a single unit and the right turbine turns freely.
Therefore, the output shaft can stop while the engine is running and can start at the zero speed, can turn at any speed. This gas turbine has two separated shafts and then called "two shaft gas turbine" or "free shaft gas turbine". Even if the output shaft is stopped, the gas generator (compressor-turbine unit) can spin at full speed, high pressure gases are continuously supplied and the high torque is produced. This type of gas turbine has high torque at low speed and comparably high efficiency at low speed, so it is suitable for propelling cars and trains.
|